Restrictions for West Virginia
Review Supervised Release restrictions in each of the federal districts and the Sex Offender Registry requirements for the state of West Virginia
Review Supervised Release restrictions in each of the federal districts and the Sex Offender Registry requirements for the state of West Virginia
Below you will find information on standard conditions of supervision and travel restrictions, as well as sex offender registry requirements.
Always follow the conditions and restrictions given to you by your U.S. Probation Officer.
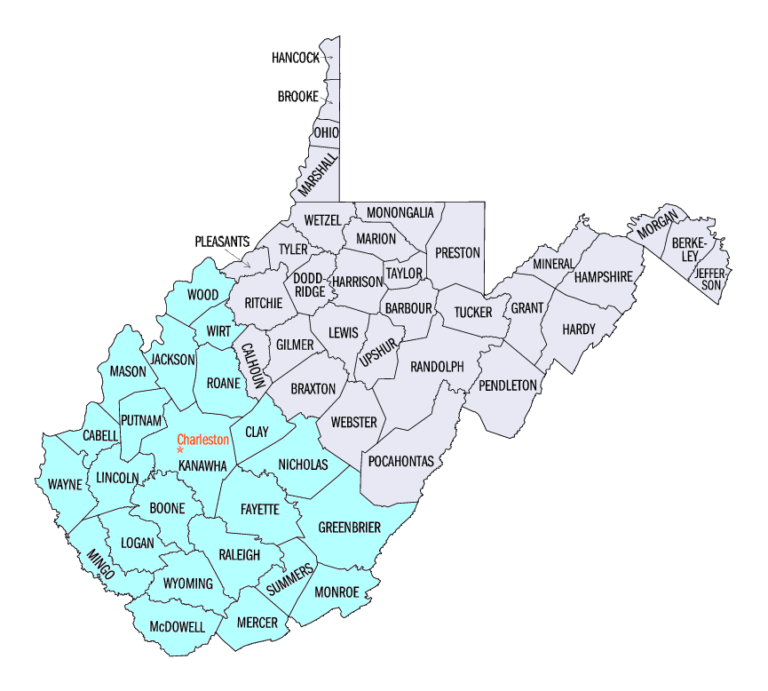
The Northern District of West Virginia is composed of 32 counties. You are allowed to travel freely within these 32 counties. Unless you are given permission in advance by the judge in your case, any requests to travel outside of these 32 counties must be approved in advance by your U.S. Probation Officer.
Failure to do so may result in a violation of your supervision.
The Southern District of West Virginia is composed of 23 counties. You are allowed to travel freely within these 23 counties. Unless you are given permission in advance by the judge in your case, any requests to travel outside of these 23 counties must be approved in advance by your U.S. Probation Officer.
Failure to do so may result in a violation of your supervision.
Every state and U.S. territory requires those convicted of sex offenses to be added to a registry to be monitored and tracked after their release back into the community. Information about the offender is collected and shared with local and federal authorities, as well as the general public. Requirements and restrictions are often placed on registered sex offenders. That registration process is unique in each state and U.S. territory.

The Sex Offender Registration and Notification Act (SORNA) was passed in 2006 as part of the Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act to provide federal standards for jurisdictions to follow. SORNA calls for states and U.S. territories to meet minimum requirements for sex offender registration and notification.
While SORNA’s guidelines streamlined registration and notification requirements across the country, these requirements are far from uniform. Each jurisdiction determines the details of their own registration process. This leaves a patchwork of rules for sex offenders that vary widely depending on where a registrant lives or works.
Probation Information Network developed a list of questions regarding the sex offender registration requirements across the country. These are questions that might concern the public, victims and their advocates, or those who are facing registration or are currently registered and their loved ones. We then searched the statutes or code of each jurisdiction for the laws surrounding sex offender registration and notification. Where necessary, we consulted with the law enforcement agency in charge of the jurisdiction’s registry to provide clear and concise answers to the following questions:
How long must a sex offender remain on the registry? The length of time a sex offender must comply with registration requirements varies widely depending on the jurisdiction where the registrant lives, and the level of the offense committed. All but 2 jurisdictions offer a path for eventual removal from the registry for at least some of their registrants.
Every jurisdiction has passive community notification in the form of a public sex offender registry website. Concerned citizens are free to search the website and can sign up for email notifications if a sex offender moves into their neighborhood. Some jurisdictions go even further and require active notification, where either law enforcement or the offender themselves is required to directly notify the immediate community that a sex offender is in the area. This can take many forms, including electronic, mail, or in-person notification, publication in local newspapers, and community meetings.
Are there any restrictions on where a registered sex offender can live? Some jurisdictions restrict registrants from living within a measured distance of certain places. This restriction could be for all registrants, or only for higher-level offenders or those under supervision. Some jurisdictions do not have a state-wide restriction but do allow local jurisdictions to enact their own.
Registered sex offenders are usually restricted from certain types of employment, and from working at establishments that specifically cater to minors. Some jurisdictions go even further and restrict registrants from working within a measured distance of certain places.
Returning citizens of every type need to find employment upon reentry, and sex offenders are no exception. Some jurisdictions include registrants’ employment information on the public registry website. This could be the employer’s address or in some cases the name of the employer.
Some jurisdictions require registered sex offenders to report any identifiers they use online, such as email addresses and social media user names. In some jurisdictions that information is included on the public registry website, separate from the registrant’s profile, in a feature that allows the public to search by specific identifiers.
Some jurisdictions require a state-issued ID, such as a driver’s license, to be labeled to identify the holder as a registered sex offender. This label could be the words “Sex Offender” printed on the ID in a prominent place or a more subtle designation known to law enforcement.
Is there a fee to register as a sex offender? Some jurisdictions pass on some of their administrative costs to the registrants. This could be a one-time fee paid only upon initial registration, or an ongoing fee paid annually or quarterly. Some jurisdictions charge a fee every time a registrant updates their information.
Does a sex offender have to register if they work or go to school in a different state? It depends on the state, and how long the registrant will be there. Some jurisdictions require registrants to notify authorities immediately, while others allow limited stays without requiring registration. Registrants currently under supervision usually need permission from their Parole or Probation Officer before traveling and should always consult their supervising officer.
Can a registered sex offender go on vacation? Does a sex offender have to register if they visit a different state? It depends on the state, and how long the registrant will be there. Some jurisdictions require registrants to notify authorities immediately, while others allow limited stays without requiring registration. Registrants currently under supervision usually need permission from their Parole or Probation Officer before traveling and should always consult their supervising officer.
The answers provided are taken directly from the laws found on the state or territory’s legislative website or, where necessary, from the website of the law enforcement agency in charge of the jurisdiction’s registry. In some cases, we contacted state or territory officials for clarification and have directly quoted those conversations.
While we stand by our research, it is for informational purposes only. It should not be considered legal advice and, while we strive to provide accurate and up to date information, it is not guaranteed to be complete or correct. We provide links to each jurisdiction’s legislative and law enforcement websites and maintain a directory of lawyers who specialize in sex offender registration laws. For those currently under supervision, consult with your Parole or Probation Officer for guidance.
WV Code § 15-12-4
(a) A person required to register under the terms of this article shall continue to comply with this section, except during ensuing periods of incarceration or confinement, until:
(1) Ten years have elapsed since the person was released from prison, jail, or a mental health facility or 10 years have elapsed since the person was placed on probation, parole, or supervised or conditional release. The 10-year registration period may not be reduced by the sex offender’s release from probation, parole, or supervised or conditional release; or
(2) For the life of that person, if that person: (A) Has one or more prior convictions or has previously been found not guilty by reason of mental illness, mental retardation, or addiction for any qualifying offense referred to in this article; (B) has been convicted or has been found not guilty by reason of mental illness, mental retardation, or addiction of a qualifying offense as referred to in this article, and upon motion of the prosecuting attorney, the court finds by clear and convincing evidence that the qualifying offense involved multiple victims or multiple violations of the qualifying offense; (C) has been convicted or has been found not guilty by reason of mental illness, mental retardation, or addiction of a sexually violent offense; (D) has been determined pursuant to §15-12-2a of this code to be a sexually violent predator; or (E) has been convicted or has been found not guilty by reason of mental illness, mental retardation, or addiction of a qualifying offense as referred to in this article, involving a minor or a person believed or perceived by the registrant to be a minor.
WV Code § 15-12-5
(b) (1) When a person has been determined to be a sexually violent predator under the terms of section two-a of this article, the State Police shall notify the prosecuting attorney of the county in which the person resides, owns or leases habitable real property that he or she regularly visits, is employed or attends a school or training facility. The prosecuting attorney shall cooperate with the State Police in conducting a community notification program which is to include publication of the offender’s name, photograph, place of residence, location of regularly visited habitable real property owned or leased by the offender, county of employment and place at which the offender attends school or a training facility, as well as information concerning the legal rights and obligations of both the offender and the community. Information relating to the victim of an offense requiring registration may not be released to the public except to the extent the prosecuting attorney and the State Police consider it necessary to best educate the public as to the nature of sexual offenses: Provided, That no victim’s name may be released in any public notification pursuant to this subsection. No information relating to telephone or electronic paging device numbers a registrant has or uses may be released to the public with this notification program. The prosecuting attorney and State Police may conduct a community notification program in the county where a person who is required to register for life under the terms of subdivision (2), subsection (a), section four of this article resides, owns or leases habitable real property that he or she regularly visits, is employed or attends a school or training facility. Community notification may be repeated when determined to be appropriate by the prosecuting attorney;
The West Virginia State Police has no legal authority to direct where a sex offender may or may not live, and additionally, unless specific court ordered restrictions exist, offenders are constitutionally free to live wherever and with whomever they choose.
– West Virginia State Police
None.
Only the names of the city and county where the registrant is employed are provided.
While offenders must register online identifiers [WV Code § 15-12-2 (d) (8)], this information is not included on the public registry.
Yes, with a code under Restrictions.
WV Code § 17B-2-3
(b) The division may not issue a license or nondriver identification card to any person required to register as a sexually violent predator pursuant to the provisions of article twelve, chapter fifteen, unless he or she obtains a driver’s license or nondriver identification card coded by the commissioner to denote that he or she is a sexually violent predator as follows:
(1) If a person is judicially determined to be a sexually violent predator after the effective date of this section, the sentencing court shall order the person or the agency with custody of the person’s driver’s license or nondriver identification card to surrender said license or card to the court. The sentencing court shall forward to the division all driver’s licenses or nondriver identification cards that it receives pursuant to this section, along with a copy of the sentencing order. If a person is registered as a sexually violent predator pursuant to section nine, article twelve, chapter fifteen of this code after the effective date of this section as amended and reenacted during the first extraordinary session of the 2006 Legislature, the person shall surrender their driver’s license or nondriver identification card to the division within ten days of their registration with the State Police. Any replacement driver’s license or nondriver identification card issued to the person under this section must be coded by the commissioner to denote the person is a sexually violent predator and shall be issued at no cost to the person.
There is no state-mandated fee, though fees may be assessed by local law enforcement.
WV Code § 15-12-9
(b) Any person:
(1) Who resides in another state or federal or military jurisdiction;
(2) Who is employed, carries on a vocation, is a student in this state, is a visitor to this state for a period of more than fifteen continuous days or owns or leases habitable real property in this state that he or she regularly visits; and
(3) Who is required by the state, federal or military jurisdiction in which he or she resides to register in that state, federal or military jurisdiction as a sex offender, or has been convicted of a violation in that state, federal or military jurisdiction that is similar to a violation in this article requiring registration as a sex offender in this state, shall register in this state and otherwise comply with the provisions of this article.
WV Code § 15-12-9
(b) Any person:
(1) Who resides in another state or federal or military jurisdiction;
(2) Who is employed, carries on a vocation, is a student in this state, is a visitor to this state for a period of more than fifteen continuous days or owns or leases habitable real property in this state that he or she regularly visits; and
(3) Who is required by the state, federal or military jurisdiction in which he or she resides to register in that state, federal or military jurisdiction as a sex offender, or has been convicted of a violation in that state, federal or military jurisdiction that is similar to a violation in this article requiring registration as a sex offender in this state, shall register in this state and otherwise comply with the provisions of this article.