Ohio Federal Districts:
Northern and Southern
Below you will find information on standard conditions of supervision and travel restrictions, as well as sex offender registry requirements.
Always follow the conditions and restrictions given to you by your U.S. Probation Officer.
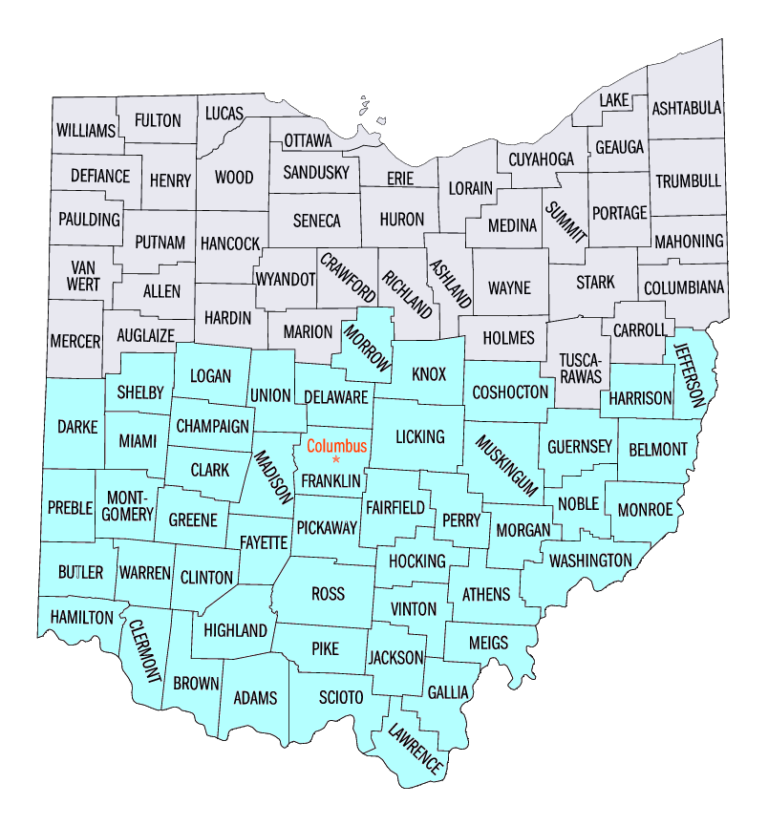
Select your district below:
Standard Conditions of Supervision
- You must report to the probation office in the federal judicial district where you are authorized to reside within 72 hours of your release from imprisonment, unless the probation officer instructs you to report to a different probation office within a different duration.
- After initially reporting to the probation office, you will receive instructions from the court or the probation officer about how and when you must report to the probation officer, and you must report to the probation officer as instructed.
- You must not knowingly leave the federal judicial district where you are authorized to reside without first getting permission from the court or probation office.
- You must answer truthfully the questions asked by your probation officer.
- You must live at a place approved by the probation officer. If you plan to change where you live or anything about your living arrangements (such as the people you live with), you must notify the probation officer at least 10 days before the change. If notifying the probation officer in advance is not possible due to unanticipated circumstances, you must notify the probation officer within 72 hours of becoming aware of a change or expected change.
- You must allow the probation officer to visit you at any time at your home or elsewhere, and you must permit the probation officer to take any items prohibited by the conditions of your supervision that he or she observes in plain view.
- You must work full-time (at least 30 hours per week) at a lawful type of employment, unless the probation officer excuses you from doing so. If you do not have full-time employment, you must try to find full-time employment, unless the probation officer excuses you from doing so. If you plan to change where you work or anything about your work (such as your position or your job responsibilities), you must notify the probation officer at least 10 days before the change. If notifying the probation officer at least 10 days in advance is not possible due to unanticipated circumstances, you must notify the probation officer within 72 hours of becoming aware of a change or expected change.
- You must not communicate or interact with someone you know is engaged in criminal activity. If you know someone has been convicted of a felony, you must not knowingly communicate or interact with that person without first getting the permission of the probation officer.
- If you are arrested or questioned by a law enforcement officer, you must notify the probation officer within 72 hours.
- You must not own, possess, or have access to a firearm, ammunition, destructive device, or dangerous weapon (i.e.., anything that was designed, or was modified for, the specific purpose of causing bodily injury or death to another person such as nunchakus or tasers).
- You must not act or make any agreement with a law enforcement agency to act as a confidential human source or informant without first getting the permission of the court.
- If the probation officer determines that you pose a risk to another person (including an organization), the probation officer may require you to notify the person about the risk and you must comply with that instruction. The probation officer may contact the person and confirm that you have notified the person about the risk.
- You must follow the instructions of the probation officer related to the conditions of supervision.
Travel Restrictions
- You are restricted to the area which constitutes the Northern District of Ohio.
- No travel outside of the Northern District of Ohio will be permitted within the initial 60-day assessment period.
- Travel outside the Northern District of Ohio is permitted only if you are in compliance with all conditions of Supervision. Offenders in special treatment programs are subject to greater travel restrictions.
- Travel Requests should be submitted in writing at least two (2) weeks in advance to allow sufficient time for verification.
- Clients who are granted travel permission should call the probation officer upon returning to the Northern District of Ohio within 24 hours.
- Travel outside the United States requires the consent of the Court or the Parole Commission.
For more information visit the links below:
Standard Conditions of Supervision
- The defendant shall not leave the judicial district without the permission of the court or probation officer.
- The defendant shall report to the probation officer in a manner and frequency directed by the court or probation officer.
- The defendant shall answer truthfully all inquiries by the probation officer and follow the instructions of the probation officer.
- The defendant shall support his or her dependents and meet other family responsibilities.
- The defendant shall work regularly at a lawful occupation unless excused by the probation officer for schooling, training, or other acceptable reasons.
- The defendant shall notify the probation officer at least ten days prior to any change in residence or employment.
- The defendant shall refrain from excessive use of alcohol and shall not purchase, possess, use, distribute, or administer any controlled substance or any paraphernalia related to any controlled substance, except as prescribed by a physician.
- The defendant shall not frequent places where controlled substances are illegally sold, used, distributed, or administered.
- The defendant shall not associate with any persons engaged in criminal activity and shall not associate with any person convicted of a felony, unless granted permission to do so by the probation officer.
- The defendant shall permit a probation officer to visit him or her at any time at home or elsewhere and shall permit confiscation of any contraband observed in plain view of the probation officer.
- The defendant shall notify the probation officer within 72 hours of being arrested or questioned by a law enforcement officer.
- The defendant shall not enter into any agreement to act as an informer or a special agent of a law enforcement agency without the permission of the court.
- As directed by the probation officer, the defendant shall notify third parties of risks due to the defendant’s criminal record or personal history or characteristics and shall permit the probation officer to make such notifications and to the defendant’s compliance with such notification requirements.
Travel Restrictions
The Southern District of Ohio is comprised of 48 counties. You are allowed to travel freely within these 48 counties. Unless you are given permission in advance by the judge in your case, any requests to travel outside of these 48 counties must be approved in advance by your U.S. Probation Officer.
Failure to do so may result in a violation of your supervision.
For more information visit the links below:
What is the sex offender registry?
What is the Sex Offender Registry?
Every state and U.S. territory requires those convicted of sex offenses to be added to a registry to be monitored and tracked after their release back into the community. Information about the offender is collected and shared with local and federal authorities, as well as the general public. Requirements and restrictions are often placed on registered sex offenders. That registration process is unique in each state and U.S. territory.

What is SORNA?
The Sex Offender Registration and Notification Act (SORNA) was passed in 2006 as part of the Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act to provide federal standards for jurisdictions to follow. SORNA calls for states and U.S. territories to meet minimum requirements for sex offender registration and notification.
Why Are the Requirements for Sex Offender Registration Different Everywhere?
While SORNA’s guidelines streamlined registration and notification requirements across the country, these requirements are far from uniform. Each jurisdiction determines the details of their own registration process. This leaves a patchwork of rules for sex offenders that vary widely depending on where a registrant lives or works.
Where PIN Comes In
Probation Information Network developed a list of questions regarding the sex offender registration requirements across the country. These are questions that might concern the public, victims and their advocates, or those who are facing registration or are currently registered and their loved ones. We then searched the statutes or code of each jurisdiction for the laws surrounding sex offender registration and notification. Where necessary, we consulted with the law enforcement agency in charge of the jurisdiction’s registry to provide clear and concise answers to the following questions:
- What is the duration of registration?
How long must a sex offender remain on the registry? The length of time a sex offender must comply with registration requirements varies widely depending on the jurisdiction where the registrant lives, and the level of the offense committed. All but 2 jurisdictions offer a path for eventual removal from the registry for at least some of their registrants.
- Must the immediate community be notified directly, either by the offender or law enforcement?
Every jurisdiction has passive community notification in the form of a public sex offender registry website. Concerned citizens are free to search the website and can sign up for email notifications if a sex offender moves into their neighborhood. Some jurisdictions go even further and require active notification, where either law enforcement or the offender themselves is required to directly notify the immediate community that a sex offender is in the area. This can take many forms, including electronic, mail, or in-person notification, publication in local newspapers, and community meetings.
- What are the residence distance restrictions?
Are there any restrictions on where a registered sex offender can live? Some jurisdictions restrict registrants from living within a measured distance of certain places. This restriction could be for all registrants, or only for higher-level offenders or those under supervision. Some jurisdictions do not have a state-wide restriction but do allow local jurisdictions to enact their own.
- What are the employment distance restrictions?
Registered sex offenders are usually restricted from certain types of employment, and from working at establishments that specifically cater to minors. Some jurisdictions go even further and restrict registrants from working within a measured distance of certain places.
- Is an employer’s information included on the public registry?
Returning citizens of every type need to find employment upon reentry, and sex offenders are no exception. Some jurisdictions include registrants’ employment information on the public registry website. This could be the employer’s address or in some cases the name of the employer.
- Are online identifiers included on the public registry?
Some jurisdictions require registered sex offenders to report any identifiers they use online, such as email addresses and social media user names. In some jurisdictions that information is included on the public registry website, separate from the registrant’s profile, in a feature that allows the public to search by specific identifiers.
- Is a state-issued ID required to be labeled?
Some jurisdictions require a state-issued ID, such as a driver’s license, to be labeled to identify the holder as a registered sex offender. This label could be the words “Sex Offender” printed on the ID in a prominent place or a more subtle designation known to law enforcement.
- What is the cost of registration?
Is there a fee to register as a sex offender? Some jurisdictions pass on some of their administrative costs to the registrants. This could be a one-time fee paid only upon initial registration, or an ongoing fee paid annually or quarterly. Some jurisdictions charge a fee every time a registrant updates their information.
- How long can a registrant be in the state for work or education before registration is required?
Does a sex offender have to register if they work or go to school in a different state? It depends on the state, and how long the registrant will be there. Some jurisdictions require registrants to notify authorities immediately, while others allow limited stays without requiring registration. Registrants currently under supervision usually need permission from their Parole or Probation Officer before traveling and should always consult their supervising officer.
- How long can a registrant visit the state before registration is required?
Can a registered sex offender go on vacation? Does a sex offender have to register if they visit a different state? It depends on the state, and how long the registrant will be there. Some jurisdictions require registrants to notify authorities immediately, while others allow limited stays without requiring registration. Registrants currently under supervision usually need permission from their Parole or Probation Officer before traveling and should always consult their supervising officer.
The answers provided are taken directly from the laws found on the state or territory’s legislative website or, where necessary, from the website of the law enforcement agency in charge of the jurisdiction’s registry. In some cases, we contacted state or territory officials for clarification and have directly quoted those conversations.
Disclaimer
While we stand by our research, it is for informational purposes only. It should not be considered legal advice and, while we strive to provide accurate and up to date information, it is not guaranteed to be complete or correct. We provide links to each jurisdiction’s legislative and law enforcement websites and maintain a directory of lawyers who specialize in sex offender registration laws. For those currently under supervision, consult with your Parole or Probation Officer for guidance.
What is the duration of registration?
ORC § 2950.07 (B)
(1) Except as otherwise provided in this division, if the person is an offender who is a tier III sex offender/child-victim offender relative to the sexually oriented offense or child-victim oriented offense, if the person is a delinquent child who is a tier III sex offender/child-victim offender relative to the sexually oriented offense or child-victim oriented offense, or if the person is a delinquent child who is a public registry-qualified juvenile offender registrant relative to the sexually oriented offense, the offender’s or delinquent child’s duty to comply with those sections continues until the offender’s or delinquent child’s death. Regarding a delinquent child who is a tier III sex offender/child-victim offender relative to the offense but is not a public registry-qualified juvenile offender registrant relative to the offense, if the judge who made the disposition for the delinquent child or that judge’s successor in office subsequently enters a determination pursuant to section 2152.84 or 2152.85 of the Revised Code that the delinquent child no longer is a tier III sex offender/child-victim offender, the delinquent child’s duty to comply with those sections continues for the period of time that is applicable to the delinquent child under division (B)(2) or (3) of this section, based on the reclassification of the child pursuant to section 2152.84 or 21562.85 of the Revised Code as a tier I sex offender/child-victim offender or a tier II sex offender/child-victim offender. In no case shall the lifetime duty to comply that is imposed under this division on an offender who is a tier III sex offender/child-victim offender be removed or terminated. A delinquent child who is a public registry-qualified juvenile offender registrant may have the lifetime duty to register terminated only pursuant to section 2950.15 of the Revised Code.
(2) If the person is an offender who is a tier II sex offender/child-victim offender relative to the sexually oriented offense or child-victim oriented offense, the offender’s duty to comply with those sections continues for twenty-five years. Except as otherwise provided in this division, if the person is a delinquent child who is a tier II sex offender/child-victim offender relative to the sexually oriented offense or child-victim oriented offense, the delinquent child’s duty to comply with those sections continues for twenty years. Regarding a delinquent child who is a tier II sex offender/child-victim offender relative to the offense but is not a public registry-qualified juvenile offender registrant relative to the offense, if the judge who made the disposition for the delinquent child or that judge’s successor in office subsequently enters a determination pursuant to section 2152.84 or 2152.85 of the Revised Code that the delinquent child no longer is a tier II sex offender/child-victim offender but remains a juvenile offender registrant, the delinquent child’s duty to comply with those sections continues for the period of time that is applicable to the delinquent child under division (B)(3) of this section, based on the reclassification of the child pursuant to section 2152.84 or 2152.85 of the Revised Code as a tier I sex offender/child-victim offender.
(3) Except as otherwise provided in this division, if the person is an offender who is a tier I sex offender/child-victim offender relative to the sexually oriented offense or child-victim oriented offense, the offender’s duty to comply with those sections continues for fifteen years. Except as otherwise provided in this division, if the person is a delinquent child who is a tier I sex offender/child-victim offender relative to the sexually oriented offense or child-victim oriented offense, the delinquent child’s duty to comply with those sections continues for ten years. Regarding a delinquent child who is a juvenile offender registrant and a tier I sex offender/child-victim offender but is not a public registry-qualified juvenile offender registrant, if the judge who made the disposition for the delinquent child or that judge’s successor in office subsequently enters a determination pursuant to section 2152.84 or 2152.85 of the Revised Code that the delinquent child no longer is to be classified a juvenile offender registrant, the delinquent child’s duty to comply with those sections terminates upon the court’s entry of the determination. A person who is an offender who is a tier I sex offender/child-victim offender may have the fifteen-year duty to register terminated only pursuant to section 2950.15 of the Revised Code.
Must the immediate community be notified directly, either by the offender or law enforcement?
ORC § 2950.11
(A) The sheriff shall provide the notice to all of the following persons:
(1)(a) Any occupant of each residential unit that is located within one thousand feet of the offender’s or delinquent child’s residential premises, that is located within the county served by the sheriff, and that is not located in a multi-unit building. Division (D)(3) of this section applies regarding notices required under this division.
(b) If the offender or delinquent child resides in a multi-unit building, any occupant of each residential unit that is located in that multi-unit building and that shares a common hallway with the offender or delinquent child. For purposes of this division, an occupant’s unit shares a common hallway with the offender or delinquent child if the entrance door into the occupant’s unit is located on the same floor and opens into the same hallway as the entrance door to the unit the offender or delinquent child occupies. Division (D)(3) of this section applies regarding notices required under this division.
(c) The building manager, or the person the building owner or condominium unit owners association authorizes to exercise management and control, of each multi-unit building that is located within one thousand feet of the offender’s or delinquent child’s residential premises, including a multi-unit building in which the offender or delinquent child resides, and that is located within the county served by the sheriff. In addition to notifying the building manager or the person authorized to exercise management and control in the multi-unit building under this division, the sheriff shall post a copy of the notice prominently in each common entryway in the building and any other location in the building the sheriff determines appropriate. The manager or person exercising management and control of the building shall permit the sheriff to post copies of the notice under this division as the sheriff determines appropriate. In lieu of posting copies of the notice as described in this division, a sheriff may provide notice to all occupants of the multi-unit building by mail or personal contact; if the sheriff so notifies all the occupants, the sheriff is not required to post copies of the notice in the common entryways to the building. Division (D)(3) of this section applies regarding notices required under this division.
(d) All additional persons who are within any category of neighbors of the offender or delinquent child that the attorney general by rule adopted under section 2950.13 of the Revised Code requires to be provided the notice and who reside within the county served by the sheriff;
(F)(1) Except as provided in division (F)(2) of this section, the duties to provide the notices described in divisions (A) and (C) of this section apply regarding any offender or delinquent child who is in any of the following categories:
(a) The offender is a tier III sex offender/child-victim offender, or the delinquent child is a public registry-qualified juvenile offender registrant, and a juvenile court has not removed pursuant to section 2950.15 of the Revised Code the delinquent child’s duty to comply with sections 2950.04, 2950.041, 2950.05, and 2950.06 of the Revised Code.
(b) The delinquent child is a tier III sex offender/child-victim offender who is not a public registry-qualified juvenile offender registrant, the delinquent child was subjected to this section prior to January 1, 2008, as a sexual predator, habitual sex offender, child-victim predator, or habitual child-victim offender, as those terms were defined in section 2950.01 of the Revised Code as it existed prior to January 1, 2008, and a juvenile court has not removed pursuant to section 2152.84 or 2152.85 of the Revised Code the delinquent child’s duty to comply with sections 2950.04, 2950.041, 2950.05, and 2950.06 of the Revised Code.
(c) The delinquent child is a tier III sex offender/child-victim offender who is not a public registry-qualified juvenile offender registrant, the delinquent child was classified a juvenile offender registrant on or after January 1, 2008, the court has imposed a requirement under section 2152.82, 2152.83, or 2152.84 of the Revised Code subjecting the delinquent child to this section, and a juvenile court has not removed pursuant to section 2152.84 or 2152.85 of the Revised Code the delinquent child’s duty to comply with sections 2950.04, 2950.041, 2950.05, and 2950.06 of the Revised Code.
What are the residence distance restrictions?
Under 2950.034(A), an offender convicted on or after July 1, 2007, is not permitted to reside within 1,000 feet of any school, preschool, or child day care center. An offender convicted between July 31, 2003, and July 1, 2007, cannot reside within 1,000 feet of any school premises. An offender convicted before July 31, 2003 is not restricted from living near a school or day care.
– Ohio Bureau of Criminal Investigation
ORC § 2950.034
(A) No person who has been convicted of, is convicted of, has pleaded guilty to, or pleads guilty to a sexually oriented offense or a child-victim oriented offense shall establish a residence or occupy residential premises within one thousand feet of any school premises or preschool or child day-care center premises.
What are the employment distance restrictions?
None.
Is an employer's information included on the public registry?
Yes.
Are online identifiers included on the public registry?
While offenders must register internet identifiers [ORC § 2950.04 (C)(10)], this information is not included on the public registry.
Is a state-issued ID required to be labeled?
No.
What is the cost of registration?
ORC § 311.171
(B) The sheriff may charge a fee each time a person does any of the following:
(1) Registers under section 2950.04 or 2950.041 of the Revised Code;
(2) Registers a new residence address under section 2950.05 of the Revised Code;
(3) Verifies a current residence address under section 2950.06 of the Revised Code.
(C) If the sheriff charges one or more fees provided for in division (B) of this section, all of the following apply:
(1) The sheriff shall not require the payment of any fee from a delinquent child until the delinquent child reaches eighteen years of age. When a delinquent child reaches eighteen years of age and the sheriff charges a fee to the delinquent child, the provisions of this section applicable to “offenders” shall be construed to apply to the delinquent child.
(2) For an offender who is a tier III sex offender/child-victim offender, the fees may not exceed a total of one hundred dollars for each registration year.
(3) For an offender who has been convicted of or pleaded guilty to a sexually oriented offense or a child-victim offense and who is not described in division (C)(2) of this section, the fees may not exceed a total of twenty-five dollars for each registration year.
ORC § 311.172
(A) The sheriff shall charge a one-time fee of one hundred dollars when a person who, on or after the effective date of this section, is convicted of an offense for which registration is required under section 2950.04 or 2950.041 of the Revised Code registers for the first time. The fee shall be in addition to any fee that may be charged under section 311.171 of the Revised Code.
How long can a registrant be in the state for work or education before registration is required?
An offender who committed his or her offense before Jan. 1, 2008, must register within five days of coming into a county where he or she is staying for five or more days. If this type of offender has worked in a county for 14 consecutive days or 30 days in a calendar year, he or she must register with the sheriff.
An offender who committed his or her offenses after Jan. 1, 2008, must register within three days of being in a county for three or more days, or for work purposes, if he or she has been in the county for 14 or more total (not necessarily consecutive) days in a calendar year.
An offender in either category (that is, regardless of date of offense) must register with the local sheriff immediately upon entering a county in which he or she attends school or an institution of higher education.
– Ohio Bureau of Criminal Investigation
ORC § 2950.04
(A)(2)(b) The offender shall register personally with the sheriff, or the sheriff’s designee, of the county immediately upon coming into a county in which the offender attends a school or institution of higher education on a full-time or part-time basis regardless of whether the offender resides or has a temporary domicile in this state or another state.
(c) The offender shall register personally with the sheriff, or the sheriff’s designee, of the county in which the offender is employed if the offender resides or has a temporary domicile in this state and has been employed in that county for more than three days or for an aggregate period of fourteen or more days in that calendar year.
(d) The offender shall register personally with the sheriff, or the sheriff’s designee, of the county in which the offender then is employed if the offender does not reside or have a temporary domicile in this state and has been employed at any location or locations in this state more than three days or for an aggregate period of fourteen or more days in that calendar year.
How long can a registrant visit the state before registration is required?
An offender who committed his or her offense before Jan. 1, 2008, must register within five days of coming into a county where he or she is staying for five or more days. If this type of offender has worked in a county for 14 consecutive days or 30 days in a calendar year, he or she must register with the sheriff.
An offender who committed his or her offenses after Jan. 1, 2008, must register within three days of being in a county for three or more days, or for work purposes, if he or she has been in the county for 14 or more total (not necessarily consecutive) days in a calendar year.
An offender in either category (that is, regardless of date of offense) must register with the local sheriff immediately upon entering a county in which he or she attends school or an institution of higher education.
– Ohio Bureau of Criminal Investigation
ORC § 2950.04
(A)(2)(a) The offender shall register personally with the sheriff, or the sheriff’s designee, of the county within three days of the offender’s coming into a county in which the offender resides or temporarily is domiciled for more than three days.